序列化利器kryo
纠错
25 Dec 2014
这几天在做一个缓存工具,其中一个目标是支持AOP,
于是有下面这样一段代码:
public class MethodCacheInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {
Object value = CacheManager.getInstance().get(invocation.getArguments());
if(null == value) {
value = invocation.proceed();
CacheManager.getInstance().put(invocation.getArguments(), value);
}
return value;
}
}
CacheManager是单例模式,方法的参数作为Key,方法的返回值作为Value。
所以,必须对Object以及Object[]进行序列化,so,采用Hessian、Kryo、Java等,可配置。
这篇文章,我们仅讨论Kryo。
接下来,我们先试用下Kryo,代码如下:
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.util.Arrays;
//
import org.junit.Test;
//
import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.Kryo;
import com.esotericsoftware.kryo.io.Output;
import com.esotericsoftware.minlog.Log;
//
public class KryoTestByjjf {
//
@Test
public void test() {
Log.TRACE();
Kryo kryo = new Kryo();
//
Output output = null;
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
output = new Output(baos);
kryo.writeClassAndObject(output, new EntityTest(23, "45"));
output.flush();
byte[] b = baos.toByteArray();
//
System.out.println(Hex.encodeHexStr(b, false)); //将byte数组转换为16进制
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));
} finally {
if (output != null)
output.close();
}
}
}
//
class EntityTest implements Serializable {
//
private int i;
private String name;
//
public EntityTest() {
}
//
public EntityTest(int i, String name) {
this.i = i;
this.name = name;
}
//
public int getI() {
return this.i;
}
//
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
}
16进制输出为:0100636F6D2E6A6A662E456E74697479546573F4012E0134B5
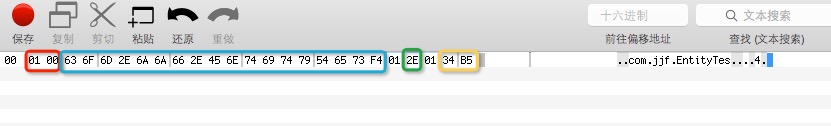
如图所示:红色部分:未注册的类
蓝色部分:类名,其中最后一位xF4是被加上了x80的,so xF4=x80+x74,查询ASCII表,x74代表t
绿色部分:x2E代表23
黄色部分:x34代表4,xB5也是被加上x80了,xB5=x80+x35,查表,x35代表5
除了圈圈中的,还有两个x01,是IdentityObjectIntMap中存储的id
下面贴出序列化int、String的代码,一看便知。
public int writeVarInt (int value, boolean optimizePositive) throws KryoException {
if (!optimizePositive) value = (value << 1) ^ (value >> 31);
if (value >>> 7 == 0) {
require(1);
buffer[position++] = (byte)value;
return 1;
}
if (value >>> 14 == 0) {
require(2);
buffer[position++] = (byte)((value & 0x7F) | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 7);
return 2;
}
if (value >>> 21 == 0) {
require(3);
buffer[position++] = (byte)((value & 0x7F) | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 7 | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 14);
return 3;
}
if (value >>> 28 == 0) {
require(4);
buffer[position++] = (byte)((value & 0x7F) | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 7 | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 14 | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 21);
return 4;
}
require(5);
buffer[position++] = (byte)((value & 0x7F) | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 7 | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 14 | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 21 | 0x80);
buffer[position++] = (byte)(value >>> 28);
return 5;
}
public void writeString (String value) throws KryoException {
if (value == null) {
writeByte(0x80); // 0 means null, bit 8 means UTF8.
return;
}
int charCount = value.length();
if (charCount == 0) {
writeByte(1 | 0x80); // 1 means empty string, bit 8 means UTF8.
return;
}
// Detect ASCII.
boolean ascii = false;
if (charCount > 1 && charCount < 64) {
ascii = true;
for (int i = 0; i < charCount; i++) {
int c = value.charAt(i);
if (c > 127) {
ascii = false;
break;
}
}
}
if (ascii) {
if (capacity - position < charCount)
writeAscii_slow(value, charCount);
else {
value.getBytes(0, charCount, buffer, position);
position += charCount;
}
buffer[position - 1] |= 0x80;
} else {
writeUtf8Length(charCount + 1);
int charIndex = 0;
if (capacity - position >= charCount) {
// Try to write 8 bit chars.
byte[] buffer = this.buffer;
int position = this.position;
for (; charIndex < charCount; charIndex++) {
int c = value.charAt(charIndex);
if (c > 127) break;
buffer[position++] = (byte)c;
}
this.position = position;
}
if (charIndex < charCount) writeString_slow(value, charCount, charIndex);
}
}
上篇:
StampedLock学习记录
下篇:
Json序列化利器FastJSON